Viruses are malicious soft wares that get transmitted to our personal computer systems and corrupt or critically damage the data present within. Viruses are equally capable of manipulating the confidential files and documents present inside the device and result in huge jeopardy of the user’s privacy and cyber experience. These fraudulent soft wares are mainly designed by cyber criminals who gain unrestricted access into the devices infected with viruses to detriment the programs present there and impose a grave threat to the cybersecurity of the concerned user.
Earlier, viruses could mainly be passed on through external hardware devices like Compact Disks that were circulated by notorious hackers and spammers to invade the privacy of the users. But, with the introduction of portable sources of networks like modems and USB, viruses are easily transmitted online through corrupted web links and web pages, false web advertisements, spam emails, etc. Once a user enters a web page encompassing virus and downloads any application pertaining to the same, his system is immediately infested with malware and can hence be ventured by the developers of that malware program, unless protected. Such unauthorized access to cybercriminals fetches hazardous implications for the owner of the computer device.
Here’s a statistic showing the impact of the most vicious viruses of all time:-
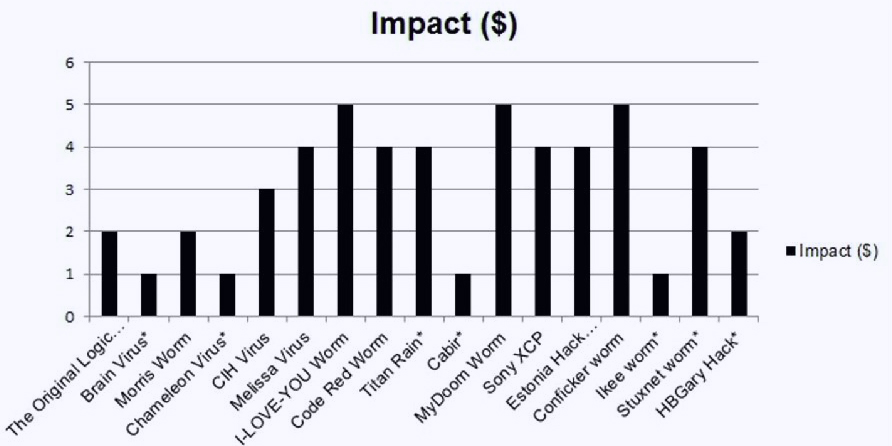
Source: Google
Which is the most dangerous computer virus of all time?
Time and again, a bewildering variety of soft wares carrying malware have been discovered by cyber experts to have irrevocably damaged the data present in a computer system. Ever since the advent of the internet, the virus Melissa was the first of its kind to get communicated via fraudulent e-mails. Melissa was developed by David L. Smith and circulated in March 1999 as a series of emails with attachment. The attachments would come with a subject like “Here is that document you asked for, don’t show it to anybody else.”It would then replicate itself into several copies and automatically forwarded to the first 50 recipients of the user’s Outlook Address Book. This virus was mainly designed to wreck the workings of the US Government via the internet network. Soon, FBI could trace down the developer Smith and come up with necessary antivirus codes that eliminated the further transmission of this online worm. Melissa, although short-lived, was one of the first kind of viruses to cause a stir on the internet and among its users.
Following the journey of Melissa, various other viruses witnessed their emergence. But, statistics over the years are to be believed; the ILOVEYOU virus remains the most destructive form of an online worm to be ever created.
About the ILOVEYOU virus application:-
Internet was compelled to be a habitat for viruses through the delivery of attached applications with duplicate emails. ILOVEYOU emerged just a year after Melissa had infected several computer systems through negligent online surfing and receiving of spam attachments via email.
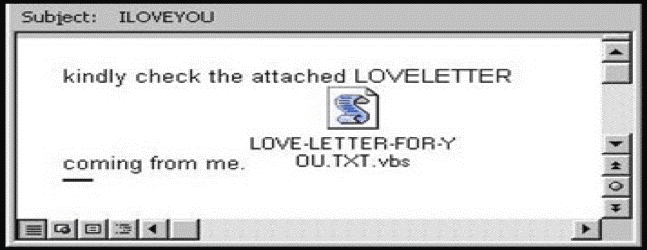
Source: Google
ILOVEYOU was designed in the Philippines during the year 2000. The alleged owner of this software application was a person named Onel de Guzman. This form of the virus was much more advanced than its predecessor that it could replicate several copies of itself and its malicious codes. It came as an attachment to an email that had the subject “I LOVE YOU” written on it. The hoax created to convey this virus was a love letter from a secret admirer. The attachment in the ILOVEYOU virus was a VBScript file. VBScript is basically a code that can be executed by Windows or Internet Explorer via the window-based script host. Attachments containing the ILOVEYOU virus came under the format of ‘vbs.exe’ with an email. This attachment, if downloaded, would further permit the hackers to have direct access to the recipient’s Microsoft Outlook Contact Information. It would then duplicate its copies and forward the same files to every contact received from the user’s Outlook contact book. Entering a computer system, it would then terminate every file present under the formats of – JPG, MP3, VPOS, JS, JSE, CSS, WSH, SCT and HTA. It would then be impossible for the user to recover these files if he had no backup of the same beforehand.

Furthermore, this virus would reset the saved pages of Internet Explorer and Windows Web Browser so that the users could not get hold of their saved information for a second time.
Here’s a brief summary of the various threats the ILOVEYOU virus had caused with its occurrence:
• It replicated itself into various copies and transferred such those copies into the different folders present in the computer’s documents.
• It spammed the user’s registry keys with similar such copies causing a breach in his security.
• It created different kinds of files with similar malware codes and replaced the other important files present in the user’s desktop with the harmful ones.
• It arranged for the conveyance of its duplicate files through the earlier chat network called “Relay Chat” and its different users as well as to several recipients via email attachments.
• It downloaded a similar fraudulent file called ‘WIN-BUGSFIX.EXE’ into the user’s system. This file rather than its claim of fixing bugs would steal important passwords and email confidential information to the cybercriminals. The criminals would further have the tendency to blackmail the owners, especially those who run a large scale business, of leaking the information in exchange for ransom.
ILOVEYOU had such a massive effect over the internet that leading companies had to shut down their email services, including the well-known Ford Motor Company.
To combat further transmission of this virus, companies warned their employees and another user’s to refrain from downloading email attachments with similar subjects. Hackers never gave in to this technique. They discovered other forms of subjects to circulate the virus continuously among the masses. Examples include – “HAPPY MOTHERS’ DAY”, “JOKE” and ironically “VIRUS ALERT – DOWNLOAD TO PROTECT YOUR FILES”
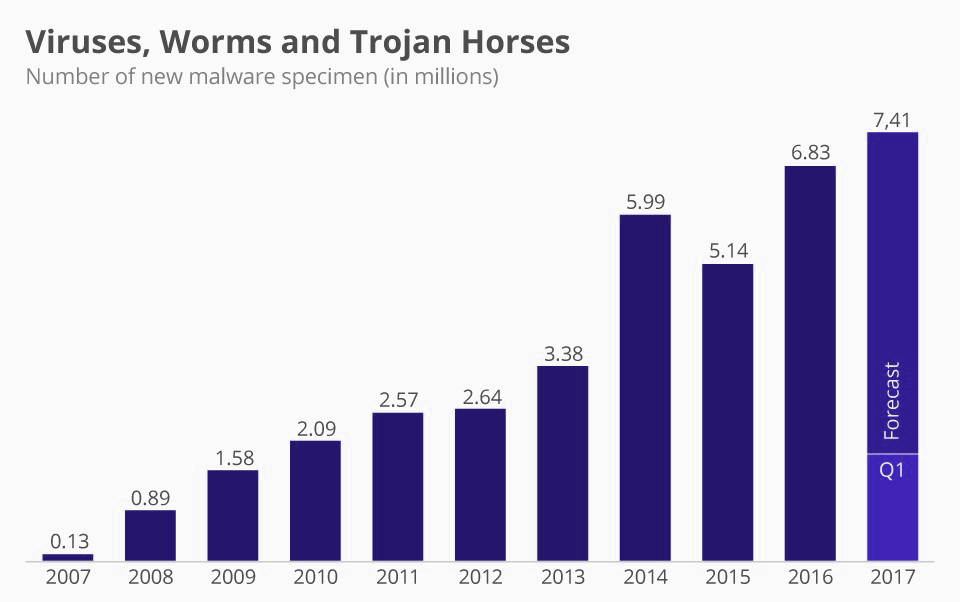
Following the footsteps of ILOVEYOU, hackers found several techniques and developed other soft wares with similar advanced features to impose a threat into the security of files and programs present within a computer system. Some of the perilous substitutes of ILOVEYOU include CODE RED, My Doom Worm, and Stutnex Worm, etc.
Statistics showing virus distribution over years. (Source – Google)
Companies providing security solutions against cybercrime hence started developing antivirus soft wares to account for a solution to this issue. These antivirus soft wares are capable of detecting files containing malware and then erasing them from the device to help protect the surfing experience of users online and their privacy offline.





















Leave a comment